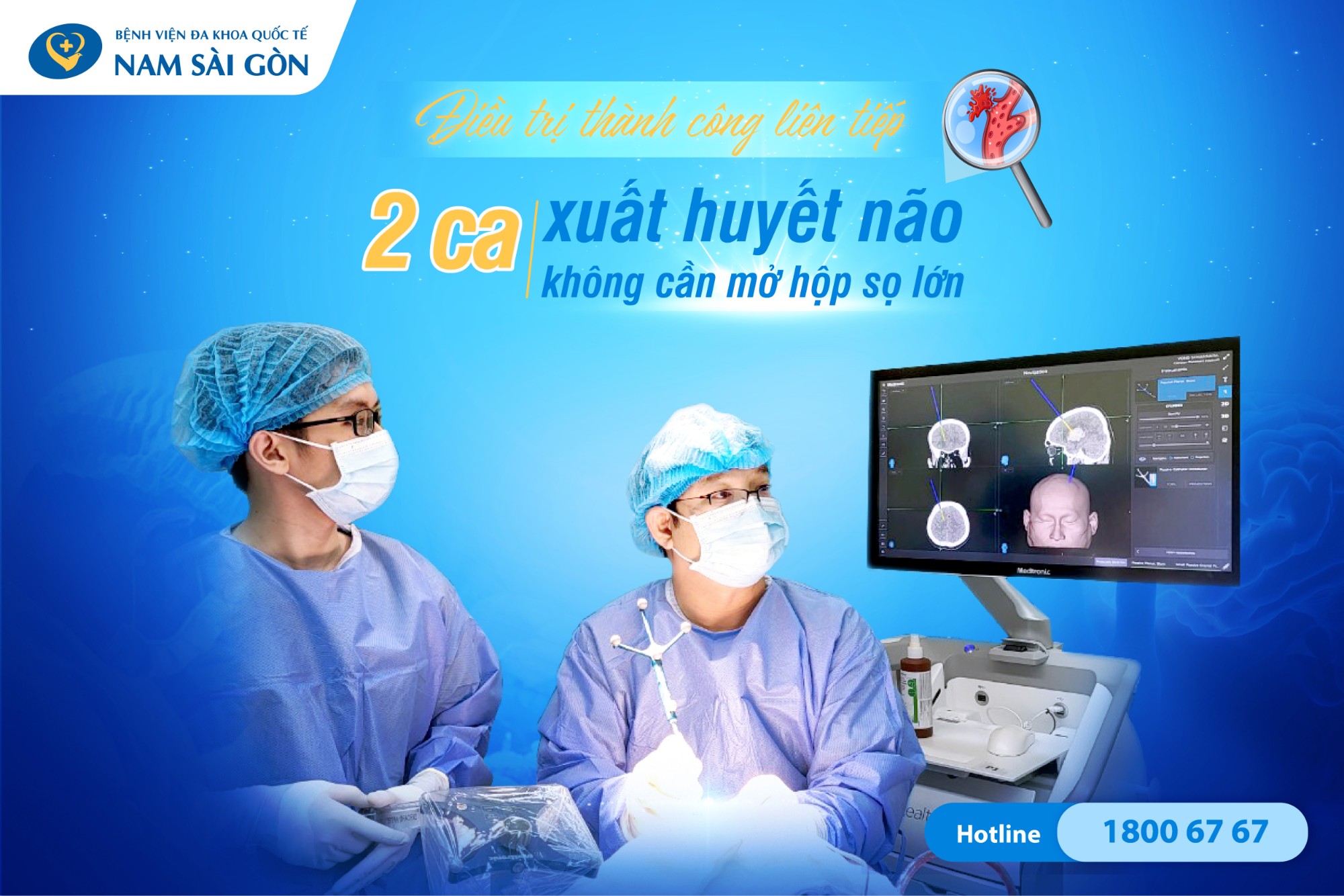
TREATMENT AND INTERVENTION FOR STROKE
-
Author: BỆNH VIỆN ĐA KHOA QUỐC TẾ NAM SÀI GÒN
-
05/09/2025
-
1,206
Stroke—also known as cerebrovascular accident—is one of the leading causes of death and disability worldwide, with more than 17 million cases reported each year according to the World Health Organization (WHO).
In Vietnam, new cases exceed 200,000 annually and are increasingly occurring in younger individuals, with cases even recorded in those under 40 years old. Understanding how to provide first aid and effective stroke treatment during the “golden hour” is crucial for saving lives and minimizing severe complications.
In this article, with professional consultation from Specialist Level I Doctor Hồ Thanh Lịch, Head of the General Internal Medicine Department at Nam Sai Gon International General Hospital, you will be guided through initial first-aid steps, advanced stroke treatment methods, estimated costs, reputable treatment locations, and answers to frequently asked questions.
1. Stroke and First Aid
1.1 What is a Stroke?
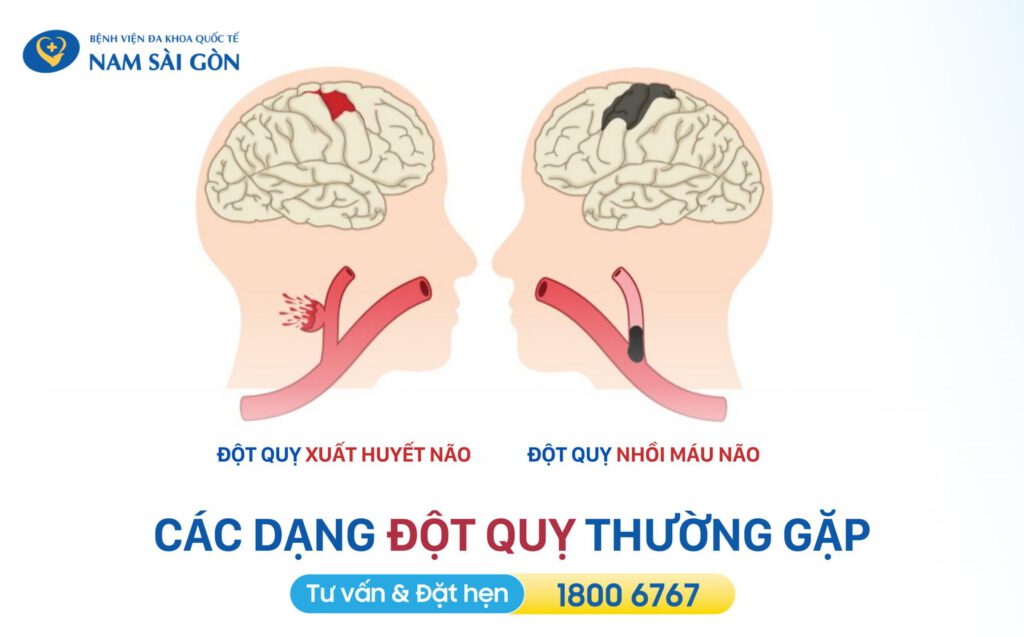
A stroke occurs when part of the brain is damaged due to a sudden interruption or reduction of blood flow. The most common causes are a blood clot blocking a vessel (ischemic stroke, accounting for about 87%) or a ruptured blood vessel leading to bleeding in the brain (hemorrhagic stroke, accounting for about 13%).
The brain is the control center of all bodily functions. When the oxygen supply to the brain is disrupted, brain cells quickly begin to die. Without timely detection and intervention, the patient may face severe consequences such as hemiplegia, loss of speech, coma, or even death.
Dr. Hồ Thanh Lịch emphasizes: “A stroke can occur in anyone—from the elderly to young adults—and the timing of intervention is the critical factor in stroke treatment.”
1.2 Initial First Aid When Encountering a Stroke Patient
Proper initial response is a crucial step in stroke management, helping reduce complications and increase the chances of recovery. “Every minute that passes during a stroke, approximately 1.9 million brain cells die. Providing correct first aid in the first few minutes can save the patient’s life,” Dr. Lịch emphasizes.
When you identify someone showing signs of a suspected stroke, quickly follow these steps:
- Call emergency services: Immediately contact 115 or take the patient to the nearest medical facility. Do not attempt to manage the situation at home, as this may worsen the condition.
- Position the patient safely: Lay the patient on their side with their head elevated about 30 degrees to prevent choking in case of vomiting and to keep the airway clear.
- Do not give food or drink: Absolutely avoid giving the patient anything to eat, drink, or any medication unless prescribed by a doctor.
- Monitor closely: Observe symptoms such as breathing and pulse, and report them to medical staff for timely support.

2. Stroke Treatment
The treatment regimen for stroke depends on the type of stroke, the extent of brain damage, and the timing of detection. The most important factor is ensuring that the patient is brought to the hospital within the “golden hour” to increase survival rates and improve recovery outcomes. Below are the detailed treatment methods:
2.1 Treatment for Ischemic Stroke
Ischemic stroke occurs when an artery supplying blood to the brain becomes blocked, usually due to a blood clot or atherosclerotic plaque. Treatment options include:
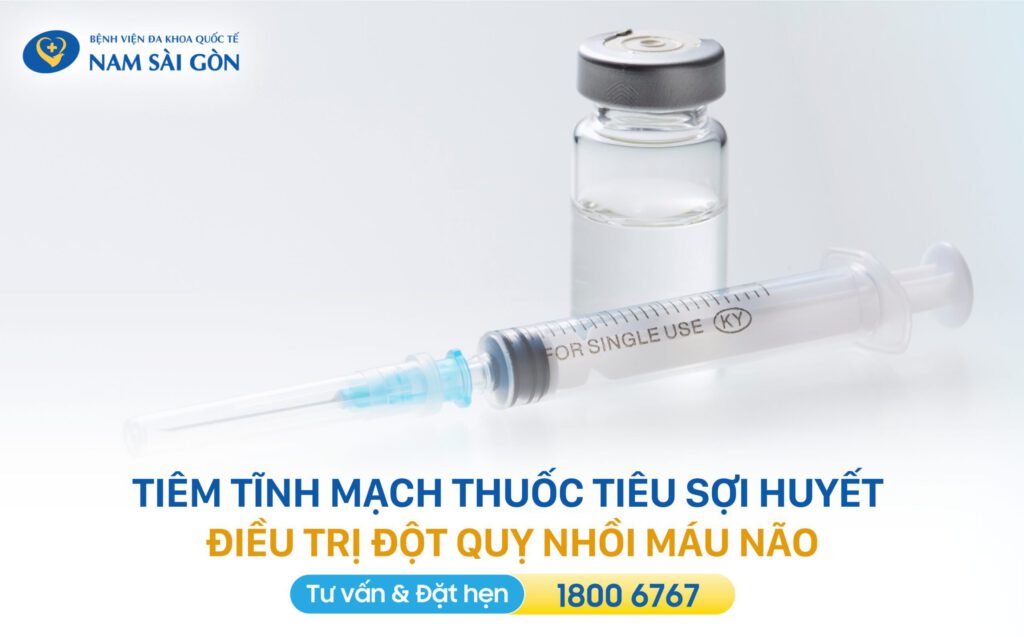
- Thrombolytic therapy (Alteplase – tPA):
Administered intravenously within the first 4.5 hours after symptom onset. This medication helps dissolve the clot and restore blood flow to the brain, but it is only effective when given early under medical supervision. - Endovascular intervention:
Applied in cases of large artery occlusion and performed within 6–24 hours of onset. Physicians use a catheter inserted into the blood vessel to directly remove the clot, offering a higher chance of recovery if performed promptly. - Supportive medications:
These include anticoagulants and medications for controlling blood pressure, blood glucose, and cholesterol to prevent recurrence.
2.2 Treatment for Hemorrhagic Stroke
Hemorrhagic stroke occurs when a blood vessel inside or around the brain ruptures, causing bleeding and increasing intracranial pressure. This condition has a high mortality rate (40–50%) and requires urgent surgical intervention.
Treatment for hemorrhagic stroke primarily focuses on:
Controlling blood pressure and intracranial pressure:
Medications are used to rapidly lower blood pressure, stabilize cerebral circulation, and reduce the risk of further damage.
Emergency surgery:
-
Aneurysm clipping or endovascular coiling: Prevents rebleeding in patients with cerebral aneurysms.
-
Hematoma drainage or evacuation: Removes accumulated blood that is compressing the brain, typically indicated in severe hemorrhage cases.
-
Repair of vascular malformations: Treats arteriovenous malformations (AVM) to prevent long-term complications.
Medical support:
Close monitoring and correction of factors such as coagulation disorders to reduce the risk of additional bleeding.

3. Post-Stroke Rehabilitation

Rehabilitation is a crucial stage in stroke treatment, helping patients regain mobility, restore communication skills, and improve their quality of life. This process typically begins soon after the patient’s condition stabilizes and may last from several months to several years, depending on the severity of the damage.
- Physical therapy:
Supports gait training, muscle strength recovery, prevention of muscle atrophy, and maintenance of flexible movement. Exercises are personalized based on each patient’s condition. - Speech therapy:
Designed for patients who have lost the ability to speak or understand language, helping them restore communication through specialized exercises. - Psychological therapy:
Helps patients cope with depression, anxiety, or emotional changes after a stroke, with guidance from mental health professionals. - Daily living skill training:
Assists patients in performing self-care activities and in using assistive devices such as canes or wheelchairs when needed.
4. Where to Receive Stroke Treatment?

To achieve optimal results, stroke patients should seek treatment at reputable medical facilities equipped with experienced specialists and modern technology. Nam Sai Gon International General Hospital is a reliable choice, offering:
- Advanced technology:
CT and MRI imaging systems, along with endovascular intervention capabilities, enabling accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. - Medical team:
Led by Specialist Level I Doctor Hồ Thanh Lịch, an experienced expert in General Internal Medicine. - Screening packages:
Including a basic package (for individuals under 40) and an advanced package (for those at higher risk).
Address: No. 88, Street No. 8, Trung Son Residential Area, Binh Hung Commune, Ho Chi Minh City.
Hotline: 1800 6767.
5. Can Stroke Be Cured?
Stroke treatment can lead to favorable outcomes if the condition is detected early—within the “golden hour” (the first 3–4.5 hours after symptom onset). During this period, the chances of survival and functional recovery are significantly higher compared to delayed intervention.
Ischemic Stroke
Patients may receive thrombolytic therapy (Alteplase – tPA) to dissolve the blood clot and restore cerebral blood flow. If a major artery is blocked, doctors may perform endovascular intervention using a catheter to remove the clot directly. When administered promptly, these two methods can help patients recover almost completely and minimize long-term complications.
Hemorrhagic Stroke
Although less common, hemorrhagic stroke has a higher mortality rate. Treatment typically focuses on controlling blood pressure, reducing intracranial pressure, and performing emergency surgery to remove hematomas or repair aneurysms. Despite being more complex than ischemic stroke management, early intervention still offers patients a chance of survival and functional recovery.
Recovery Potential and Complications
The level of recovery after a stroke depends on various factors: type of stroke, the location and size of the affected brain area, age, underlying medical conditions, and the speed of emergency response. Some individuals may return to near-normal daily activities, while others may face long-term complications such as:
-
Hemiplegia or persistent muscle weakness
-
Speech disorders, difficulty speaking, or loss of communication abilities
-
Memory impairment and emotional changes
-
Dependence on others for daily living activities
Stroke can be treated, but this does not mean every case will fully recover. The decisive factor is how quickly the patient is brought to the hospital for proper diagnosis and treatment. Choosing a reputable medical facility equipped with modern technology and a highly specialized team greatly increases the chances of survival and reduces long-term complications. After the acute phase, patients require rehabilitation and long-term follow-up to reduce the risk of recurrence and improve their quality of life.
6. Frequently Asked Questions About Stroke Treatment
6.1 Can Stroke Be Treated at Home?
No. Treating a stroke at home is extremely dangerous and strongly discouraged. Stroke is a medical emergency that requires immediate professional intervention, such as thrombolytic therapy or surgical procedures. Self-medicating or using folk remedies can worsen the condition and may even lead to death. Call emergency services immediately when stroke symptoms are detected.
6.2 How Much Does Stroke Treatment Cost?
The cost of stroke treatment depends on various factors, such as the type of stroke (ischemic or hemorrhagic), the intervention method, the patient’s condition at admission, and the length of hospital stay.
Typically, treatment costs include the following components:
-
Initial consultation and diagnostic tests (CT scan, MRI, blood tests, clinical examination).
-
Emergency treatment (thrombolytic medication, endovascular intervention, or surgery if needed).
-
In-hospital care and monitoring, including hospital bed, medications, and supportive services.
-
Post-stroke rehabilitation, such as physical therapy, speech therapy, and psychological therapy.
Costs may vary significantly depending on each specific case. Therefore, patients and families should consult directly with a reputable hospital for detailed advice and to prepare an appropriate financial plan.
Dr. Ho Thanh Lich advises: “The cost of stroke treatment may vary, but saving lives and minimizing complications should always be the top priority. Contact the hospital directly for personalized consultation based on the patient’s condition.”
6.3 How Long Does Stroke Recovery Take?
Recovery time depends on the extent of brain injury and the treatment methods applied:
-
Mild cases: 1–3 months with physical therapy and home care.
-
Moderate cases: 6–12 months, often requiring speech and psychological therapy.
-
Severe cases: 1–2 years or longer, with potential permanent complications such as hemiplegia.
Recovery is more effective when combined with proper nutrition, regular exercise, and routine medical check-ups to monitor progress.
Nam Sai Gon International General Hospital
No. 88, Street No. 8, Trung Son Residential Area, Binh Hung Commune, Ho Chi Minh City.
Hotline: 18006767
info@nih.com.vn
Last updated: 16:30 08/12/2025
1. Mayo Clinic | What is a stroke? A Mayo Clinic expert explains | Neurologist Robert D. Brown, Jr. M.D., M.P.H.
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/stroke/symptoms-causes/syc-20350113
2. U.S Centers For Disease Control And Prevention | About Stroke.
https://www.cdc.gov/stroke/about/index.html
3. National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute | Stroke.
https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/stroke
4. Health Direct | Stroke – Last reviewed: December 2024.
https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/stroke
5. Cleveland Clinic | Stroke | Medically Reviewed – Last reviewed on 01/27/2025.
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/5601-stroke
6. Healthline | Everything You Need to Know About Stroke | Medically reviewed by Nancy Hammond, M.D. — Written by Kimberly Holland — Updated on June 5, 2025.
https://www.healthline.com/health/stroke
Articles on the same topic